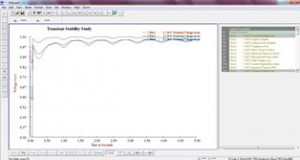
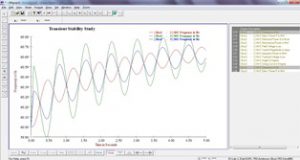
With the disturbances being the integral part of the power systems, it is vital for the system operator to understand the impact of these disturbances, from stability perspective, on the operational performance of the critical infrastructure like generators. The accurate transient response is critical for evaluation of the stability under large disturbances like faults.
The key features of the module are :
- Supports LG/LL/LLG/LLL/ LLLG fault at user defined location
- Detailed representation of
- Turbines governors and Excitation systems (AVR)
- Power System Stabilizers (PSS)
- Static VAr compensators (SVC), HVDC controllers
- Load Shedding as disturbance
- Simulation of voltage / current / frequency and distance relays
- Large Motor Starting Analysis
The studies enable the assessment of variations in operational parameters like Voltage, Current, generator frequency and rotor angle against limits. Remedial actions are planned accordingly.
uration Machine voltage plots
yCurves
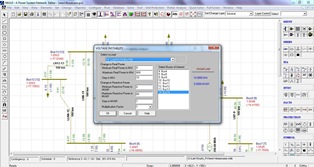
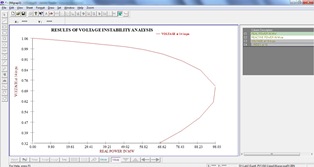
With the exploitation of the network to it’s maximum due to resource constraints, the computation of the risk of voltage instability gaining importance. Voltage Instability analysis assess the proximity to the critical point (Loadability limit) and also computes the margin, under steady state conditions. The ranking of the load buses based on the L-index value indicate the weak buses in the system and the largest L-index value indicates the proximity to the system collapse point.
The key features of the module are :
- Voltage instability assessment using L-Index and Centroid Voltage methodologies
- Stability margin computation under steady state condition
- Identify weak buses and areas in the system from Voltage Instability perspective
PV and QV curves are plotted for better visualization.
stability Analysis
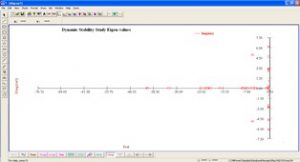
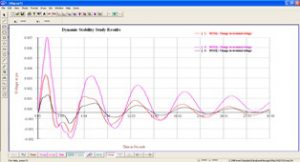
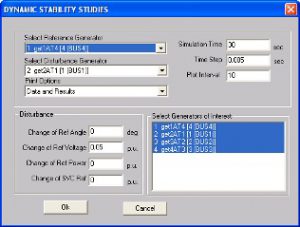
Dynamic stability indicates the ability of synchronous generators to adjust to small changes in load. The moving generators oscillate due to load change and normally settle to new values. It is important to analysis the generation oscillations and power swing oscillations to understand the small signal or dynamic stability. The amplitude and frequency of oscillations depend on the operating condition and inertia of the system.
The dynamic stability analysis is carried out in Frequency domain (Eigen value analysis) and Time domain with slow disturbances.
The key features of the module are :
- Identification of the mode of oscillation
- Examine the most effective control location
- Adjustment in control parameters to improve system damping
- Simulate disturbances to understand potential risk of oscillatory instability
configuration